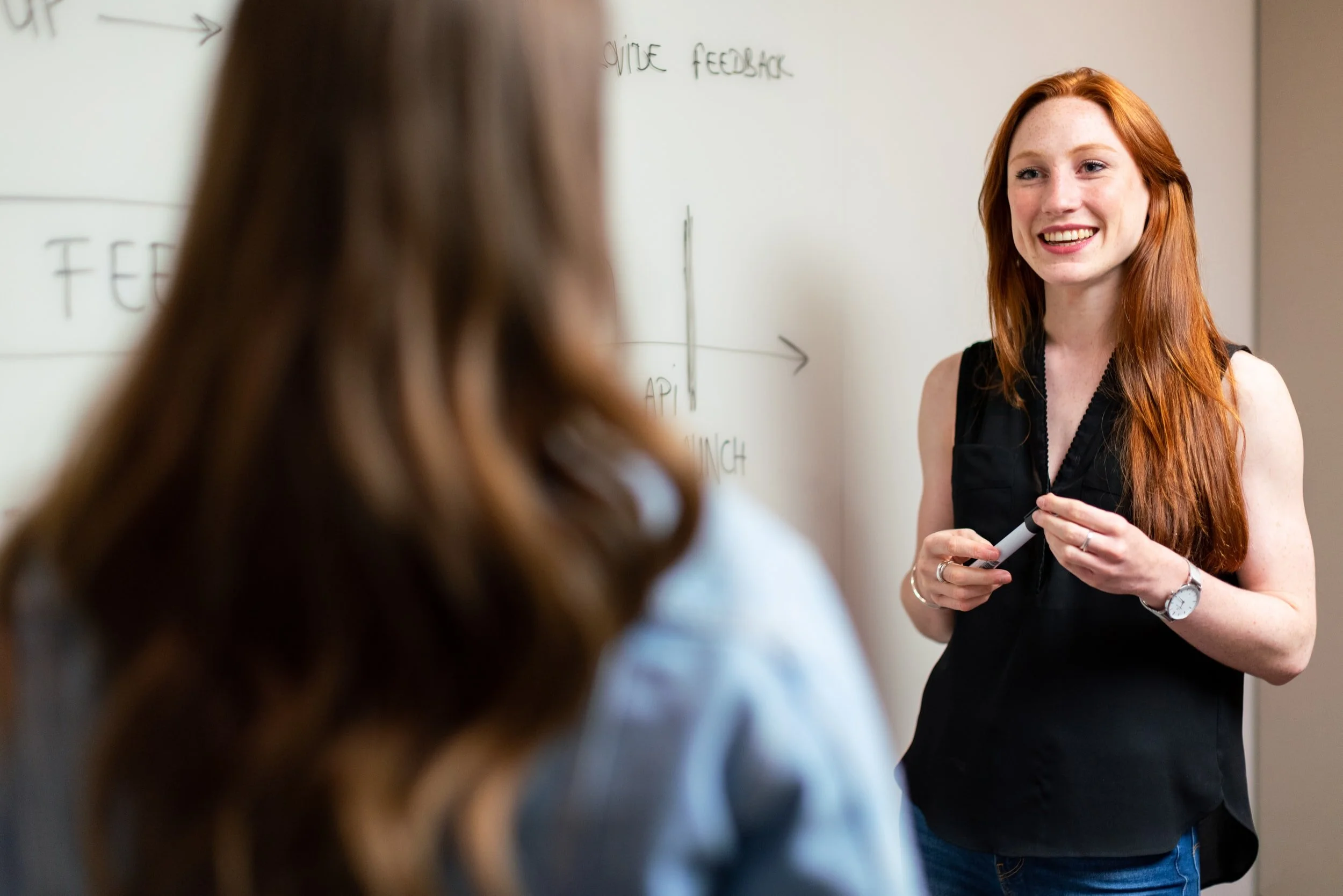In this guide, we will unravel the mysteries surrounding ACT scores, shed light on the factors that determine a “good” score, and provide invaluable insights into achieving your academic aspirations. Whether you’re a student aiming for the Ivy League or contemplating the best approach to standardized testing, this guide will navigate you through the nuances of ACT scores, helping you make informed decisions about your college journey.
What is Dual Enrollment?
Dual enrollment allows high school students to take college classes while they are still enrolled in high school.
These classes count for both high school and college credit. High school students who complete dual enrollment classes generally take fewer classes in college and save money on total college costs.
How to Teach Your Kids Success By Failing Forward
As adults, we know we don’t have all of the answers. We fail, we make mistakes, and we struggle. But if we have the mindset that we can learn from these mistakes and failures, then we persevere and get better. Too many times, though, we get stuck in the pervasive idea that failure is bad, unacceptable. There’s even tag lines quoting “Failure is not an option”. The problem with this thinking is, if failure is not an option, then how do we ever progress forward?
More to do: Students are rebounding but haven’t recovered from COVID-related learning disruptions
More to do: Students are rebounding but haven’t recovered from COVID-related learning disruptions
There are encouraging signs in newly available student achievement data from the 2021–2022 school year: evidence the nation’s education system is rebounding from the pandemic but has not yet recovered.
Students showed growth on the MAP® Growth™ assessments in reading and math at rates that are comparable with prepandemic times. They also recovered some lost ground, but the extent of the improvement varies widely by grade level and student group. That’s a positive change from 2020 to 2021, when student growth slowed significantly due to COVID-19 disruptions.
These signs of rebounding show that the hard work of educators and students is paying off. However, we’re still not where we need to be.
Growth is up but not enough, and patterns vary
To get a picture of student achievement two-and-a-half years into the pandemic, NWEA researchers Megan Kuhfeld and Karyn Lewis, analyzed MAP Growth scores for more than eight million students in grades 3–8 in about 25,000 public schools across the country. They looked at achievement and growth trends for students who were in school during pandemic years, so from 2018–2019 through 2021–2022. They then compared the performance of those students to that of students in school from 2015–16 to 2018–2019, non-COVID-19 years.
Here’s what the researchers found:
There are signs of academic rebounding.
Gaps between current and prepandemic achievement have narrowed compared to spring 2021.
Achievement is still lower than we’d expect it to be absent the pandemic, particularly for historically marginalized students.
We’ve made critical strides as a nation, but COVID-19 is having a lasting impact, and the time it will take for students to catch up varies greatly across grade, subject, and student group. This research estimates it will take the average elementary-school student at least three years to catch up and much longer for older students if the rate of change continues at the same pace. You can explore this research in depth by reviewing the research brief.
Continued urgency
While we’re pleased to see evidence of academic rebounding, fully regaining lost ground will require students to make above-average progress going forward. The federal government has provided nearly $200 billion in funding for schools to address challenges associated with the pandemic, with $22 billion specifically dedicated to learning recovery using evidence-based interventions.
With the estimated timeline of recovery extending past the spending deadlines, education leaders and policymakers must scale programs that are working. Leaders must also plan for how they will sustain recovery efforts beyond September 2024, as it will take some districts, schools, and students additional time to fully recover.
Research estimates it will take the average elementary-school student at least three years to catch up and much longer for older students if the rate of change continues at the same pace.
Leaders must also continue to do more to address the persistent educational achievement inequities that existed prior to the pandemic. Returning students to prepandemic achievement levels will not be enough to close these long-standing disparities. Unless growth far exceeds average rates for hardest hit students, a lasting impact of the pandemic will be even bigger opportunity gaps and increased inequity in our education system.
What you can do
Below are steps school and system leaders and policymakers should consider taking to further spur student learning, along with examples of innovative recovery efforts happening around the country.
Invest in expanding instructional time for students, including high-quality summer programs. Summer programs are especially critical for groups of students who, even in nonpandemic years, lose more ground than others when school is out, a phenomenon known as “summer slide.” Programs must be accessible and high quality. When they are successful, they should scale. For example, the Indy Summer Learning Labs, a summer-learning initiative in Indianapolis, led to such clear learning gains that leaders expanded it. Teachers are compensated well, the program is free, instruction is rigorous, and it is aligned to standards. Students also participate in fun activities that boost engagement and participation.
Identify and target interventions for students most impacted by the pandemic. The NWEA policy and advocacy team recently led a Twitter chat on addressing COVID-related opportunity gaps, and participants said students with the highest needs must be the top priority. The federal government also has said a focus should be on disproportionately impacted student groups. One example of how this is happening at the state level is in Colorado, where a program that provides grants for high-impact tutoring to address unfinished learning prioritizes underserved students for whom COVID-learning gaps may exacerbate pre-existing inequities. In addition to targeting students who have been most impacted, it is also critical to “right-size” recovery efforts and use evidence to determine whether the positive impacts of the interventions being implemented will be enough to fully address the impacts of the pandemic.
Use data and strong data systems that provide continuous feedback on interventions to inform recovery. Collecting meaningful and timely data is essential. Educators and leaders need to use a variety of assessment data and other school- and district-level data in ways that inform decision-making and instructional practices. Data should shed light on achievement, attendance, measures of engagement, opportunities to learn, and who is receiving specific interventions. Some districts, such as Guilford County Schools in North Carolina, have developed or adopted tools like apps that teachers can download on their phones or laptops to make it easier to track enrollment and attendance in recovery programs. States should make such resources readily available. At the state level, North Carolina has allocated funds for researchers to collect, analyze, and report on the impacts of COVID-19 on schools and students.
Support teachers with the resources and professional learning opportunities they need to help their students succeed. The latest growth data shows educator efforts are paying off. A priority for this coming school year and beyond must be to support the success and well-being of teachers. In a recent Educators for Excellence survey sponsored by NWEA, educators highlighted the obstacles they’re facing. They said students’ mental health needs are far greater than before the pandemic and called on leaders to hire more counselors and mental health providers and do more to meet the needs of underserved students. Among other changes teachers want to see are greater access to high-quality curriculum, stepped-up leadership opportunities, better compensation, and assessment reporting systems that distinguish between material taught and untaught, a tool NWEA is developing. Teachers have been heroes in the pandemic. Let’s respond by giving them the support and resources they need.
Five ways parents can help children have a better school year
New!: Virtual Boot Camp & Get Ahead Programs
Our subject tutoring program provides students with one-to-one individualized support in math, science, reading, writing, English, history, and foreign language. For more information on this program, please visit our Subject Tutoring page.
Helping Students Recover from COVID-19 Setbacks
On the surface, the ongoing impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic are obvious: more than 50 million Americans have been sick and more than 900,000 have lost their lives. Small businesses have shuttered, millions have lost jobs and nearly everyone in the U.S. has been affected in one way or another.
But there are deeper impacts as well – and it may take a generation before we truly understand all of them. This is especially true of the pandemic’s effect on education. And that uncertain post-COVID future is why we need to work together right now so we can help students bounce back.
Addressing COVID-19 Learning Disruptions
Addressing COVID-19 Learning Disruptions:
Four Recommendations for
Effective Tutoring Interventions
As more students return to in-person learning, education leaders are working not only to rebuild school communities and help students transition, but also to address gaps in learning resulting from COVID-19 disruptions. One strategy states and districts are considering is tutoring, or focused instruction provided to students in one-on-one or small group settings.
Research suggests that tutoring programs can meaningfully increase learning for K–12 students and are especially effective in increasing the achievement of students who are at risk for poor learning outcomes. A range of studies shows that many tutoring programs generated learning gains in reading and mathematics, with greater gains attained in reading at early grades and math at older grades. The U.S. Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences (IES) signaled the importance of building the research based on tutoring programs and scaling up effective interventions when it launched Operation Reverse the Loss in late 2020. IES received $100 million from the American Rescue Plan to conduct research related to learning disruptions caused by COVID-19.
Recommendations for Choosing and Implementing Tutoring Interventions
Tutoring Supports in States
In 2020, the Tennessee Tutoring Corps recruited 1,000 college students to tutor students entering grades 1–4 during the summer to address student learning needs.
With support from federal funds, the Louisiana Department of Education launched a $1 million initiative to create a library of supplemental tutoring lessons aligned to state curriculum standards in English and math.
Leaders in Maryland and Oklahoma have announced plans to leverage federal stimulus funds to create grants to address the impact of COVID-19, and identified tutoring as one of the approaches that families and schools may use.
Texas is developing high-quality instructional materials to address student learning needs that can be used in summer learning programs and other learning settings.
The American Rescue Plan includes $129 billion in education funding for new programs and interventions designed to address the impact of the pandemic on student learning. To that end, here are four recommendations to help leaders interested in exploring the use of evidence-based tutoring interventions to accelerate student learning and address pandemic-related learning disruptions.
1. Use evidence-based tutoring models.
Before implementing a broad-scale tutoring program, education leaders should examine the demonstrated effectiveness of different tutoring models and programs to ensure that they are backed by evidence. Evidence-based practices are practices informed by research that lead to improved educational outcomes. Systematic reviews of the research on tutoring have found that “high dosage” tutoring—tutoring that happens in a one-on-one relationship or in small groups at least three times a week—generates positive gains for students in reading and math. In addition, a brief from the Annenberg Institute at Brown University describes design principles for effective tutoring based on rigorous education research, and it covers tutor-to-student ratios, tutoring frequency, focus, and curriculum.
Education leaders can leverage a number of resources to identify evidence-based tutoring models and practices. The What Works Clearinghouse reviews existing education research on various education programs and practices to identify “what works” in education. Its resources include a rapid review of the evidence on distance learning that includes studies of online and computer-based tutoring programs.
Further, the National Center on Intensive Intervention, led by AIR, has developed a series of charts to help educators and families select academic and behavioral assessment and tutoring intervention tools. Resources from the center include a chart comparing research on various academic interventions; an overview of the Taxonomy of Intervention Intensity, which helps educators ensure tutoring interventions are aligned to students’ needs; and a suite of companion resources focused on the taxonomy.
2. Ensure tutors are qualified to deliver the selected model.
Delivering a tutoring lesson to an individual student or small group of students calls upon different skills than those needed to deliver a lesson to a large class of students.
Education leaders will also need to consider the workforce required to implement a larger-scale program and ensure a fit between the type of intervention and staff training and skills. Delivering a tutoring lesson to an individual student or small group of students calls upon different skills than those needed to deliver a lesson to a large class of students. Systematic reviews of tutoring programs have found that tutoring efforts generally are more effective at increasing student learning when led by teachers. However, some evidence-based interventions have been validated with tutors who may not be certified teachers, such as non-teacher school staff, college students in the education field, and service fellows. Recent studies suggest that tutoring programs that use AmeriCorps members and paraprofessionals can be as effective as teacher-led programs in one-to-one or small group settings. Further, research shows that tutoring offered by nonprofessional and family members benefits students, but the benefits are smaller than for tutoring conducted by professionals or paraprofessionals
Leaders should consider the type of training needed to build tutors’ content knowledge and facilitation skills, as well as the ongoing supports that tutors will need throughout their relationship with students. Parents and family members who provide additional academic support may especially benefit from clear, accessible materials that provide scaffolding for how to engage and work with a child on a given learning task.
3. Create conditions for learning.
We know that all students have the potential to thrive when they experience safe, equitable, and engaging learning environments. Building strong, positive relationships between tutors and students can generate meaningful outcomes for students beyond academic gains. Drawing from a synthesis on the science of learning and development, the SoLD Alliance partners have articulated whole-child design principles for education systems; the first principle is that learning environments should support positive developmental relationships that we know have the potential to increase students’ sense of belonging and connection at school.
Given the contexts and experiences that students and tutors alike will bring to the table, education leaders should equip tutors with support and guidance so that they cultivate meaningful relationships with students to bolster their resiliency and engage them in learning—within the tutoring context and beyond.
4. Monitor and support quality implementation.
Carefully designing and implementing tutoring programs—as well as setting up rigorous monitoring systems—can allow education leaders to adjust and target interventions to the greatest needs.
Broader scale efforts to implement tutoring services have taught us that leaders need to monitor implementation. A good example of this is the No Child Left Behind Act of 2001, which provided funding for students in Title I schools to access tutoring services. Many states did not have the capacity to monitor the supplemental education services being offered, nor could they conduct more rigorous evaluations of the programs to understand their efficacy. Carefully designing and implementing tutoring programs—as well as setting up rigorous monitoring systems—can allow education leaders to adjust and target interventions to the greatest needs.
Leaders may want to review materials from the National Center on Intensive Intervention, which identified five considerations for the effective implementation of an intervention: student engagement, program specificity, adherence to the intervention plan, quality of delivery, and the duration of the intervention. Tools from the center can support educators as they implement and monitor interventions and assessments.
Throughout the lifecycle of the tutoring program, leaders can incorporate practices from continuous improvement science to collect data, build in flexibility, make adjustments, and reflect on what’s working—and what’s not. In our work with district and school leaders through the District and School Improvement Center, we have found this approach allows leaders not only to implement and monitor ongoing feedback loops, but also to make data-based decisions that lead to improvement for all students.
Next Steps
Just as the COVID-19 pandemic has lasted longer than many of us anticipated, education leaders also should be prepared that the process of recovery and rebuilding from the pandemic also will take time. The federal stimulus funding for K-12 education provides an opportunity for states to invest in new programs and opportunities, and leaders must consider both the scalability and sustainability of these programs to meet students’ needs for academic support—and understand that these needs may extend beyond 2021. These investments also provide an opportunity to build the lasting capacity of the education system to provide universal and intensive, individual supports and leverage research to accelerate student learning.
Vint Hill Educational Services offers small pod tutoring for grades K-12. Students can work with a tutor in a small group setting of 2-5 students. Sessions can take place at our offices, a local library, in student homes, at public facilities, or virtually through Lessonspace. The students in the pod should be enrolled in the same class or currently studying the same subject. Multiple subjects can be covered in the same pod. Special pod tutoring rates apply. Please contact us to learn more.
Tips for Academic Success
Time Management
Time management can be a challenge for some students mainly because they overestimate the amount of time they have for a task and underestimate how much time it will take for them to do it. Allowing enough time to get ready for class, study for an exam or complete an assignment can be tricky. The key is to always do what must be done first such as studying, and doing what can wait later on. For example, if you’re getting ready for class, resist checking texts, emails or searching the web. Do those more pleasurable things after the task at hand is completed. This simple strategy reduces a lot of stress that comes with last minute rushing.
Organization:
In order to maintain organization, students should schedule a “clean sweep” session to organize their binders and backpack. Set aside 20-30 minutes weekly. Sunday evening after dinner is a good time as it will help to get organized and plan ahead for the coming week. Program these reoccurring dates into your cell phone as a reminder.
Record assignments on a paper or electronic calendar even if your teachers post them online. Record the final due date and then set self-imposed incremental due dates and associated tasks to get it done. Research indicates that when big tasks like studying for a test are broken down into explicit, manageable chunks, they are more likely to be completed. For example, if a test is coming up on Friday, the student should record tasks like “complete 1-4 review problems on page 23” and “create flashcards for vocab terms”, etc. on Monday, Tuesday, or Wednesday. These specific tasks are far superior to writing down something vague like “study for test”.
Remember, no task you record should be more than 30 minutes. It’s a proven fact that when a task that takes over 30 minutes is on an individual’s “to do” list they are far more likely to procrastinate and avoid it.
For students who are not in the habit of consistently writing down assignments, utilizing an app can really help. - https://myhomeworkapp.com/ and - http://istudentpro.com/
Focus:
Whenever possible, change the homework location from time to time. Some students do better in the hum of a busy area. Those people work well in study groups, at Starbucks, or in a more public area. Others know they must have silence. These students often do better in the library. Regardless, change the location daily. The best place to study is actually outdoors!
In order to resist temptations like texting, put your phone across the room or in another room and leave it there. That way, if you want to check your texts, you have to physically get up and walk over to retrieve it. Many students report that this significantly limits the amount of texting distractions that typically occur. If this is hard for you, set the timer for 20 minutes and work as hard as you can during that time. When the timer goes off, get up, check your messages for one minute, and then get back to work. Set the timer again. A study at Stanford has shown this approach to be highly beneficial for students.
Believe it or not, there’s a direct correlation between the number of windows a student has open at the bottom of the screen and his or her GPA. The more windows, the lower the GPA and the fewer windows, the higher the grade point average. Having too many windows open decreases focus and when individuals are unfocused, they spend less time studying and their memory retrieval is impacted. Reduce the amount of windows open at the bottom of your screen as much as possible.
When students are having a hard time getting started with homework, it’s always a good idea to begin with an easy assignment, followed by a hard one, and then an easy task again. This helps get work completed with less stress. In essence, the student is being rewarded with an easy task after completion of a difficult assignment.
Reading and Studying:
Many students equate reading with studying, but simply reading is not studying because it is too passive. Reading must be interactive or it will not work when preparing for an exam. Active reading strategies include margin notes and highlighting. As reading becomes more challenging, these strategies aid students in comprehending more advanced topics.
Whether you are assigned reading or you want to review text to study for a test, read one section at a time. After you’re done with a passage, go back and highlight the most important information. Studies have shown that the color of the highlighter does not matter; it’s personal preference.
Most importantly, engage in “self talk” at the end of each section or passage. This means that the student should ask his or herself, “What did I just read?” or “What’s important here?” Self talk helps students focus and comprehend better.
Margin notes are another interactive way of studying and are far superior to merely reading the information. In brief sentences or phrases, summarize the main points in the margins of novels or text books. The act of writing improves retention.
If you are reading a text book online or hard copy, try the SCAN pre-reading strategy. Before reading:
S = Survey Headings and Turn Them into Questions
Find each bold heading, and turn it into a question.
C = Capture the Captions and Visuals
Glance at the pictures or diagrams and read each caption.
A = Attack Boldface Words
Now, focus on the bolded terms, quickly reading these words to gain an understanding of the main idea concepts.
N = Note and Read the Chapter Questions
2021-2022 MOCK ACT/SAT TEST DATES
WE WILL BE PROCTORING TESTS VIRTUALLY ON SATURDAY MORNINGS AT 9:00 AM. UPON REGISTERING FOR A VIRTUAL MOCK TEST, YOU’LL RECEIVE A TEST PACKET VIA USPS MAIL.
PACKET INCLUDES:
ACT/SAT ANSWER SHEET
ACT/SAT TEST BOOKLET
TEST INSTRUCTIONS
PLEASE SIGN UP NO LATER THAN MONDAY DURING THE WEEK OF THE MOCK TEST. BE SURE TO INCLUDE YOUR ADDRESS DURING REGISTRATION, SO THAT WE CAN MAIL YOU A TESTING PACKET.
ALL ACT/SAT TESTS WILL BE PROCTORED VIRTUALLY THROUGH LESSONSPACE. THE DAY BEFORE EACH TEST, STUDENTS WILL RECEIVE AN EMAILED LINK TO JOIN THE VIRTUALLY PROCTORED TEST. THE TEST INSTRUCTIONS CAN BE USED SHOULD A STUDENT LOSE CONNECTION TO THE TESTING LOBBY. PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A WORKING BUILT-IN MIC (OR A HEADSET) AND AUDIO ON YOUR LAPTOP/DESKTOP.
ACT
Register for a mock ACT by clicking on a specific test date below.
Mock ACT test dates:
SAT
Register for a mock SAT by clicking on a specific test date below. :
Mock SAT test dates:
We also offer one-to-one mock testing at our offices. This consists of a full-length practice test for your child. Tests include: ACT, SAT, PSAT, SSAT, ISEE, HSPT, and SAT Subject Tests. We provide the test booklet, essay booklet, answer sheet, testing timer, calculator, and pencils.
We can send parents a practice test as well, to administer to their student in-home. We will send out a free practice test packet along with proctoring instructions. Parents must send the answer sheet back to us via email or mail.
Mock ACT and SAT (Group Testing)
TESTS INCLUDE
ACT and SAT
$25 Registration Fee (1 Mock Test: ACT or SAT) Includes test scores comparison
Mock testing for the ACT and SAT, held in a group setting. Parents will receive a diagnostic score report and phone consultation. View sample student score reports: ACT and SAT.
For the ACT and SAT, we will compare scores in order to determine which test is better for the student to take. See virtual mock test dates above for the 2021-2022 school year.
In-Office or In-Home Testing (One-To-One)
TESTS INCLUDE
ACT, SAT, PSAT, SSAT, ISEE, HSPT and SAT Subject Tests
$125 Standard Test (In-office)
$175 Special Accommodations (In-office)
FREE Parent Administration (In-home)
One-to-one testing at our offices or in-home testing proctored by a parent. A perfect fit for students that need to get acclimated to the test format, structure, and timing. This can help to relieve nervousness and anxiety. Parents have the option of administering the test to their child for free. They can also choose to drop their student off at our offices and we will administer the test to the student. Parents will receive a diagnostic score report from our testing software.
4263 Aiken Drive Suite 102, Warrenton, VA 20187
Phone: 540-680-4004 Email: contact@vinthilles.com
Website: www.vinthilles.com
15 Tips to Choosing a Tutor
In recent years, and especially during COVID, the private tutoring industry has booming in the U.S. As a result, there are plenty of tutors out there, so the question is, how do you find the right one for you? We’re here with a list of the best way to choose your perfect tutor. Read on to find out more.
How to Choose a Major
Coaching vs. Tutoring
The Difference Between Tutoring and Academic Coaching
Does your child need academic help outside the classroom? Tutoring might be a good option. But you may also hear about academic “coaches” who help teach kids learning strategies.
What’s the difference? Which is best suited for your child?
There’s no official distinction between what makes one person a tutor and someone else a coach. Sometimes it’s just a matter of marketing.
Instructors may call themselves “coaches” because some students may not like the idea of being “tutored.” That’s because some students may associate being tutored with having some kind of weakness. But they may be open to being “coached,” like an athlete, to become “even better.” This is especially true for middle-schoolers and high-schoolers.
There tend to be some basic differences between the two groups, though. The information below can give you an idea of what they are.
Tutoring vs. Academic coaching — Basic approach
Tutors tend to focus on building concrete skills and helping students with what they immediately need to keep up with schoolwork.
Similar to a sports coach, an academic coach tends to work on strategies to help kids succeed. They can help kids develop a more organized approach to learning and schoolwork. They may also focus on strategies to help kids with motivation.
What a typical session may look like
A tutor may zero in on specific skills that are giving a student trouble. A math tutor, for instance, may focus on long division, going over assigned homework and helping the student get ready for upcoming tests.
Tutors can help kids work on specific skills during the summer, too. They may do practice drills so a student can keep up on skills and be ready for the new school year.
Coaches working with younger kids may help them organize their backpack. Coaches might also show kids how to create color-coded systems for notebooks and folders.
Middle- and high-schoolers may learn to create schedules that will help them tackle long-term projects. The coach may share tips and strategies about how to stay focused and take tests more effectively.
Who offers it
There’s no official credential for being a tutor. Many tutors are current or retired teachers who work independently or as part of a commercial tutoring program. But even high school students can be tutors.
Some tutors are certified to help kids with learning differences like dyslexia. They may be certified through programs like Wilson or Orton–Gillingham, or may be an educational service like Vint Hill Educational Services. Online tutoring and tutoring software are options, too.
There’s no official credential for being a learning coach or academic coach. Many are current or retired teachers, or they may have some background in education or psychology.
Some commercial tutoring centers are starting to offer more “coaching-style” programs. But they still tend to refer to these programs as tutoring services.
Type of student who could benefit
Tutoring could be a good option for students struggling to stay at grade level. It could also benefit students who need help reaching academic goals in one or more specific areas like reading, writing, science, or math. However, some students with learning differences may need to see someone more specialized, like an educational therapist.
Coaching could be helpful for students who have certain skills but lack the motivation, organization, or strategies they need to apply those skills. Coaching could also benefit students who need help with staying focused, such as kids with ADHD. Athletes with positive sports experiences often respond well to a coaching model.
Grade-schoolers who need to learn good study habits could benefit from an organizational coach. Older students who need help with prioritizing, staying on task, or even prepping for the ACT or SAT could also benefit from an academic coach.
Duration of services
Tutoring is sometimes used on a “spot” basis. This could be to help a student through a rough patch or with a specific skill, like solving quadratic equations. But tutoring often continues throughout the length of a particular course, such as algebra or chemistry.
Some coaches sell “packages” that are designed to lay the basic groundwork students need to succeed within a limited window of time. This can be anywhere from 3 to 6 months, or beyond.
Rates
Rates vary by area but are comparable to those for academic coaches.
Rates vary by area but are comparable to those for tutors.
In real life, the line between coaching and tutoring can be blurry. Some tutors, like coaches, may focus on learning strategies. Some coaches, like tutors, will help students tackle homework. And some coaches may not even call themselves “coaches.”
Once you know what kind of help your child needs, a good way to find the right person is to seek referrals from the school or other parents. Then interview each candidate carefully about what the basic approach would be. Having a list of key questions to ask can be helpful.
And be sure to let the person you hire know about your child’s strengths and weaknesses . That will let the coach or tutor do a better job of helping your child.
DOES YOUR CHILD STRUGGLE WITH STAYING ORGANIZED, PLANNING SCHOOLWORK, OR STUDYING FOR EXAMS? CONTACT US FOR A FREE COACHING ASSESSMENT.
Vint Hill Educational Services offers academic coaching for students who have difficulty getting motivated, staying focused, or keeping up in school. With backgrounds in counseling, mentoring, teaching, and special education, our coaches are highly experienced at working with youth and helping students overcome a wide spectrum of challenges.
Academic coaching is especially beneficial for individuals with attentional problems, low executive functioning, or learning or cognitive disabilities—though it is also valuable for those struggling to deal with the ordinary stressors of understanding complex information, planning assignments, studying for exams, or transitioning to college. Students who work with an academic coach typically require guidance and assistance in:
· Getting and staying organized
· Planning coursework and managing time effectively
· Starting and completing schoolwork
· Studying and reading with proficiency
· Managing stress, anxiety, and distractibility
· Balancing academic and personal responsibilities
· Preparing for tests
Our coaches complete assessments to identify the student’s challenges, strengths, goals, and learning style. They then create customized plans that integrate a variety of tools and techniques to help build confidence and improve school performance. Strategies include positive reinforcement, setting achievable goals, optimizing skills, breaking down tasks, creating a supportive environment, and tracking progress.
We select the best coach for your child and provide a coach profile for you to review and approve. The coach matching process considers the coach’s education, experience, and personality, as well as the student’s issues, schedule, and preferred location (e.g., home, office, public library). Each session is one hour in length and one-to-one for individualized support. Parents receive access to our online Teachworks system, allowing them to review coaching session notes, receive session email reminders, and keep track of used and remaining session hours.
EXECUTIVE SKILLS AND READING COMPREHENSION
The role of executive functioning in learning has been researched for many decades, and we now know that executive skills play important roles in literacy learning, and especially in successful reading comprehension. In the book by Kelly Cartwright, Executive Skills and Reading Comprehension: A Guide for Educators (2015, Guilford Press), the author explores this connection in detail and provides suggestions for supporting students who have weak executive skills.
Cartwright explains:
“Children who have difficulties with reading comprehension, despite having age-appropriate word reading skills, have lower levels of executive skills than their peers with better comprehension. These discoveries are important for all educators because reading comprehension is the foundation for all other learning in school: students cannot understand, enjoy, or respond to literature without effective reading comprehension; likewise, students cannot gather new information from science, math, or social studies texts when they don’t understand what they read. (p.3)”
What are executive function skills and how do they support reading comprehension?
Cartwright suggests we think of the term executive skills as an umbrella term that refers to a set of mental tools we use to manage tasks and achieve goals, and that these skills can be grouped into three core areas: cognitive flexibility, working memory, and inhibition.
Executive skills involve regulating one’s own thinking to achieve desired goals. Cartwright notes that “Executive skills emerge early in life and develop across childhood and beyond. Even in very young students, executive skills enable the self-control that is necessary to remember classroom routines, pay attention to a teacher’s direction, and inhibit inappropriate behaviors.”
Here is a summary of how these core skills affect reading comprehension (p. 8-9):
Cognitive Flexibility: is the ability to shift attention from one activity to another or to actively switch back and forth between important components of a task. When reading, skilled comprehenders actively shift focus between many things, such as word and text meanings, letter-sound information, and syntactic (sentence grammar) information.
Working Memory: is the capacity for holding information in mind while working with part of that information. When building text meaning, a good comprehender must keep in mind the various text ideas presented, note the causal links between them, and update the meaning as he encounters new ideas in text.
Inhibition: is the ability to resist engaging in a habitual response as well as the ability to ignore distracting information – i.e., to think before acting. Good comprehenders must inhibit activation of inappropriate word meanings or irrelevant connections to ideas encountered in texts.
Cartwright also addresses additional, more complex executive skills:
Planning: involves setting and working toward a goal
Organizing: involves ordering and sequencing information or subtasks in ways that support a common goal
You cannot reach a goal without a plan, and you can do so most effectively if you are aware of the steps you need to take, in the proper order, to ensure that your goal is met. These two skills work hand-in-hand to support reading comprehension. Good readers begin with a plan and goals to understand and they organize their approach to reading.
In addition, Cartwright points out that the level of a student’s executive skills will also affect his motivational or social-emotional processes – i.e., differences in students’ executive skills will be reflected in both their cognitive and social-emotional ability. For example:
Students with strong executive functioning ability are able to effectively manage and control their own behavior, regulate thinking and learning, regulate their emotional processes, have peer relations, and have strong emotional processes.
Students who are impulsive and emotionally reactive have difficulty controlling their own behavior, interacting with peers, sticking to classroom routines, focusing on task, and ignoring irrelevant information.
Here are some of the chapters in Cartwright’s book:
Plans and Goals: Getting Ready to Read
Organization: Why Text and Reader Organization Matter
Cognitive Flexibility: Juggling Multiple Aspects of Reading
Working Memory: Holding and Linking Ideas in Mind While Reading
Inhibition and Impulse Control: Resisting Distractions to Support Comprehension
Social Understanding: The importance of Mind Reading for Reading Comprehension
Other Resources Related to Executive Functioning and Reading
If you are interested in this topic, it is highly recommend you review the work of Lynn Meltzer at The Research Institute for Learning and Development. Her book Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom (2010, Guilford Press) provides very useful suggestions for understanding and assessing executive function processes and creating a classroom wide executive function culture that fosters strategy use for reading. Meltzer has chapters on goal setting, planning, organizing, remembering, flexible problem solving, self-monitoring, and emotional self-regulation. Meltzer and her colleagues have also developed the SMARTS Executive Function curriculum designed to help middle and high school students who have weak executive skills.
Here are a few other sources to learn more about the connection between executive skills and reading comprehension:
Why Executive Function is a Vital Stepping-Stone For Kids’ Ability to Learn: blog article at KQED News
The Reading Brain: Executive Function Hard at Work: article at LDA of America website
5 Ways Executive Functioning Issues Can Impact Reading: article at the Understood for Learning and Attention website
DOES YOUR CHILD STRUGGLE WITH STAYING ORGANIZED, PLANNING SCHOOLWORK, OR STUDYING FOR EXAMS? CONTACT US FOR A FREE COACHING ASSESSMENT.
Vint Hill Educational Services offers academic coaching for students who have difficulty getting motivated, staying focused, or keeping up in school. With backgrounds in counseling, mentoring, teaching, and special education, our coaches are highly experienced at working with youth and helping students overcome a wide spectrum of challenges.
Academic coaching is especially beneficial for individuals with attentional problems, low executive functioning, or learning or cognitive disabilities—though it is also valuable for those struggling to deal with the ordinary stressors of understanding complex information, planning assignments, studying for exams, or transitioning to college. Students who work with an academic coach typically require guidance and assistance in:
· Getting and staying organized
· Planning coursework and managing time effectively
· Starting and completing schoolwork
· Studying and reading with proficiency
· Managing stress, anxiety, and distractibility
· Balancing academic and personal responsibilities
· Preparing for tests
Our coaches complete assessments to identify the student’s challenges, strengths, goals, and learning style. They then create customized plans that integrate a variety of tools and techniques to help build confidence and improve school performance. Strategies include positive reinforcement, setting achievable goals, optimizing skills, breaking down tasks, creating a supportive environment, and tracking progress.
We select the best coach for your child and provide a coach profile for you to review and approve. The coach matching process considers the coach’s education, experience, and personality, as well as the student’s issues, schedule, and preferred location (e.g., home, office, public library). Each session is one hour in length and one-to-one for individualized support. Parents receive access to our online Teachworks system, allowing them to review coaching session notes, receive session email reminders, and keep track of used and remaining session hours. For more info, click here.
We offer one-to-one in-home test prep which encompasses all subject areas. This is ideal for students looking to achieve the largest score increases. Tutoring sessions are customized based upon the student’s strengths and weaknesses, which are revealed by having the student take one of our practice baseline tests or by submitting official score reports from previous tests. Our 36-hour program includes unlimited full-length practice test reports, unlimited course books, session notes for parents, and weekly homework assignments. Virtual prep is available through Lessonspace. Tutors can also meet students at our offices, local libraries, outdoor parks, or nearby coffee shops. *Our test prep tutors must pass ACT/SAT/SSAT/ISEE/HSPT diagnostic tests before being hired. We hand-pick the best tutor for your child based upon our matching process.
Combat the “Covid-19 Slide”
How Tutoring Programs Can Combat the “Covid-19 Slide”
The current pandemic has led to unprecedented disruptions in student learning in the United States. Remote learning, decreased instruction time, and fewer opportunities for personalized interactions with teachers have set the stage for widespread learning loss, also referred to as the “Covid-19 slide.” These risks are greatest for low-income students, students of color, and students who were already in need of additional support before schools closed their doors. As the education system works to stabilize and adapt, addressing learning loss must stay at the forefront of the conversation. Policy and education officials must be proactive in identifying strategies to combat the growth of preexisting inequities and gaps in educational access and achievement. Rigorous research indicates that tutoring — supplemental one-on-one or small group instruction — may be one of the most effective tools they can employ.
J-PAL North America’s new publication, “The transformative potential of tutoring for PreK-12 learning outcomes: Lessons from randomized evaluations,” summarizes a meta-analysis of 96 randomized evaluations of different tutoring programs. Drawing primarily from research in high-income countries, this publication examines the effectiveness of tutoring programs across a variety of characteristics, including tutor type, subject, student grade, and others. The meta-analysis finds that tutoring programs have consistently large, positive impacts on students across this range of program aspects. The magnitude and consistency of the findings point to tutoring as one of the most agreed-upon and impactful tools available to educators for improving student learning.
The review identifies valuable insights and trends across five categories.
Program effectiveness: Across all studies included in this analysis, tutoring programs consistently lead to large improvements in learning outcomes for students, with an overall pooled effect size of 0.37 standard deviations. (Effect sizes greater than 0.3 standard deviations are considered to be large impacts, especially in the context of education interventions.) This impact translates to a student advancing from the 50th percentile to nearly the 66th percentile.
Tutor type: Tutoring programs led by teacher or paraprofessional tutors are generally more effective than programs that use nonprofessional (volunteer) or parent tutors. Paraprofessional tutors include, among others, non-teacher school staff, undergraduate and graduate students in education, and service corps fellows. Paraprofessional programs led to positive effects of nearly the same magnitude as teacher programs and were more consistent in their outcomes. This presents a potentially cost-effective option for highly impactful programming.
Student grade level: The effects of tutoring programs tend to be strongest among students in earlier grades, although a smaller set of programs at the secondary level was also found to be effective at improving learning outcomes.
Subject material: While overall effects for math and reading tutoring programs are similar, reading tutoring tends to be relatively more effective for students in preschool through first grade, while math tutoring tends to be more effective for students in second through fifth grade.
Time and location of tutoring: Tutoring programs conducted during school tend to have larger impacts than those conducted after school. Many programs shown to have weaker effects used parents as tutors or took place in an after-school program. Researchers hypothesize that it is difficult to ensure that tutoring actually occurs in these settings.
This publication is meant to serve as a resource for supporting student learning and minimizing the growth of academic disparities during the Covid-19 slide. In addition to highlighting tutoring as an effective educational tool, it also identifies meaningful trends to inform how tutoring programming can be implemented most effectively. Finally, the publication outlines key open questions about how to effectively scale tutoring programs, support older students, and make tutoring accessible to the students who need it most. J-PAL North America is seeking to answer some of these questions through their COVID-19 Recovery and Resilience Initiative.
We also invite you to explore how Vint Hill Educational Services can help if you need greater flexibility in the how, when, and where of your educational journey. We have a consistent record and demonstrated success of helping students improve their grades, scores, and overall academic functioning. In addition, all our programs are taught by highly qualified teachers and tutors. You can find out more about us by visiting our website or calling us directly at 540-680-4004. We're always happy to talk with you about your options and how we can help.
Switching to Homeschooling Mid-Year
You may be thinking about switching from public school to homeschool mid-year. It’s more common than you think to switch from public to homeschool at the semester break, but you can really make the change anytime you feel it is necessary for your family.
Here are a few tips for making the switch to help you get started, and hopefully make the transition much smoother for your entire family!
Help Your Kids Focus
For families navigating the challenges of the coronavirus era, it can seem a bit like a play in three acts — only in this case, all the acts are happening at once. You are a parent, you are a teacher and you are a professional — all at the same time. Understandably, things don’t always go smoothly. The novelty of having school at home may be wearing a bit thin. So, how do we keep our kids academically engaged — and happy about it?
9 Tips on Preparing Teens for Independence
We love our children. Yet, the goal for our teens is to become self-sustaining adults, who move out of our house, and exude confidence and success without us. Right? With the academic curriculum demands of the day, it is hard to prioritize additional skills and knowledge that ensure they have been introduced to what matters the most—LIFE SKILLS.
The fact is, many basic “adulting” concepts can be missing in our youth and we don’t always know what our children don’t know. The easiest way to incorporate some life skills into daily activities is to have a QOD (Question of the Day). Questioning allows review of life skill topics, in small doses, to ensure there are no gaps. Then teaching or re-teaching, as needed, can occur. (Plus, you never know what other path of knowledge these questions will take you on.)
Turn the following 9 life skill topics into questions and get started on helping teens avoid frustration for not knowing …
1. Making Introductions
Most teens know that introducing oneself to someone involves a greeting, stating their name, and ending with a pleasantry (e.g., Hi! My name is Beth Carey. So, nice to finally meet you). However, your teen may not know the rule for introducing others is to always say the most important or higher-ranking individual’s name first. (e.g., Dad, I would like you to meet my friend Emily).
In the United States, good eye contact and a handshake would follow (or elbow bump currently) and then “small talk” (polite conversation about unimportant matters). Small talk is not something that comes naturally for any generation so don’t hesitate to practice this task.
2. Reading an Analog Clock, a Ruler, and Telling Military Time
You may chuckle here, but have you checked these skills with your teenager lately? Our digital world has created a generation (or two) that cannot read a face clock, yet alone tell military time (like the rest of the world). And ruler reading is good to the 1/4, 1/2, 3/4 markings, but if you review 7/8ths or 3/32nds you could be surprised. Tackle each task on separate days.
3. Ability to do Tasks related to General Home Life
change a furnace filter
change bed sheets & make a bed
clean a bathroom, the kitchen, & a window (w/out smears)
do laundry (include emptying lint filter)
handle an overflowing toilet & use a plunger
load and run dishwasher
locate & turn off main water valve, locate main power breaker box & reset breakers o plan & make a meal
set a table properly
sew on a button
4. Dining Protocols
Most teens love eating, but they need etiquette knowledge beyond eating out of the drive-thru bag to avoid embarrassment when eating with others (especially on special nights like proms and weddings). Things like napkin placement, when to start eating, passing food guidelines, how to indicate when you are finished with a meal, how to tip properly, and so on.
5. Job Hunting
Adolescents often want to work but get intimidated by the process. Making a list of job lead sources (signs, company websites, employment agencies, school placement offices, etc.) and identifying interests and skills a person has to offer an employer is a great way to start. Review rules for filling out an application, appropriate interviewing attire (hint: one step above company dress code), practice/plan for common interview questions, and create a resume. Include skills for writing a thank you note after an interview.
6. Writing Thank You Notes
Notes for gifts, dinner engagements, condolence gestures, or any kindness shown to a person needs to happen and ASAP, as you know. But does your adolescent know to include what they are thankful for and a related piece of info to the note? Do they realize that electronic words of gratitude are better than nothing, but handwritten notes are better? (Check their ability to address an envelope properly too.)
7. Managing Money
Start your kids on fiscal independence by helping them take control of their own money. Click here to read why every teen needs a bank account. A good and easy start is the Greenlight app. Discuss budgeting, banking, saving, using Venmo/Paypal/Zelle, writing & cashing checks, balancing an account, and building good credit. After all, “You must gain control over your money or the lack of it will forever control you”—Dave Ramsey.
8. Rules of Social Decorum when Online and Texting
There are several guidelines to know under this topic, but the #1 rule for cell phone use is to step away from others as no one wants to hear your conversation or watch you text.
When it comes to online decorum, avoid personal, serious, and emotional topics … save those for in person dialogue.
9. Ability to do Tasks related to Car Maintenance
fill car with gas & pay
check tire pressure & change a tire
add wiper fluid & change blades
jump a dead car battery with cables
check fluids
———————————————————————————————————————————
We are here to support! As we handle the academics, this gives you time to ensure they are ready for “the world”. See our blog here for more info on tutoring and test prep during the pandemic.
What this all means
Since that last day of school in March, 2020, our lives have been turned upside-down. We’ve all had to learn how to cope with staying at home when we want to go out, and students have had to learn to navigate new modes of learning through technology and virtual platforms. Now the pace is beginning to pick up, and this may leave some students behind either academically in general, or in their progress towards bigger goals such as college entrance, advanced diplomas, and career paths.
Vint Hill Education has always prided itself on working closely with students and families to find individual students’ strengths to meet the challenges of academic life, and our approach to these times is no different. We have always taken the time to communicate with parents and help shape learning plans so that the student’s needs are met and exceeded. And now more than ever, Vint Hill Education is ready and poised to offer support and guidance in navigating an ever-changing academic, test-prep, and college entrance environment. Our expertise can make the difference between a mediocre school year and one that is full of discoveries of new interests, approaches, and pursuits—truly the “silver-lining” of the Covid-19 school year.
See below or click here for more information on Virtual Tutoring, Pod Tutoring, Subject Tutoring and Academic Coaching, or Test Prep with our individualized, highly qualified, hand-picked tutors.
____________________________________________________________________________
Virtual Tutoring
Vint Hill Educational Services offers virtual tutoring through our online learning center. No matter where you live, you can work with a qualified test prep or subject specialist tutor! We also offer virtual academic coaching for students who need help with organization and time management. Our virtual tutoring provides the same individualized attention as our regular services. Sessions are one-on-one and personalized to each student’s specific needs. And students who pursue virtual test prep with us receive a full set of course books, as well as tailored homework assignments, full practice tests, and diagnostic score reports generated by our test scoring software.
Virtual tutoring sessions are held through Lessonspace and integrated with our parent/student Teachworks portal. Families receive free access to an actual virtual tutoring platform. With the click of one link, students can easily join their online sessions. There is no software to download; Lessonspace simply utilizes your web browser to host sessions.
Lessonspace was created for the sole purpose of online tutoring, so it is more comprehensive than other online meeting programs when it comes to tutoring sessions. Tutors and students have access to a white board where they can upload reading passages, math problems, science diagrams, full-length practice tests, Spanish homework, history papers, or any other subject materials a tutor and student may need to share. Session image recording is included, so students have the ability to review wok from previous sessions. Materials uploaded to the white board can be accessed by both the tutor and the student for direct and immediate interaction and feedback.
___________________________________________________________________
Small Pod Tutoring
Vint Hill Educational Services offers small pod tutoring for grades K-12. Students can work with a tutor in a small group setting of 2-5 students. Sessions can take place at our offices, a local library, in student homes, at public facilities, or virtually through Lessonspace. The students in the pod should be enrolled in the same class or currently studying the same subject. Multiple subjects can be covered in the same pod. Special pod tutoring rates apply. Please contact us to learn more.
SMALL GROUP SIZE
Pod tutoring involves small groups working with a single tutor. Students must be taking the same class or studying the same subject. For test prep pod tutoring, the students must share similar baseline scores. Other tutors can be brought in if the students are studying multiple subjects. For example, the pod may work with a Spanish tutor on Monday, and then switch to working with a Chemistry tutor on Wednesday.
STUDY TOGETHER AS ONE
Pod tutoring allows for a small group to work together alongside their pod tutor. Questions and ideas are bounced off one another with the main instruction being provided by the pod tutor. Being in a pod, new concepts are instilled as a small group, and creativity is always encouraged. Students are comfortable asking questions and feel less nervous around their pod peers.
LOW-COST ALTERNATIVE
Pod tutoring is an alternative for one-to-one tutoring and families can save money by utilizing small pod tutoring. The tutoring expense is shared among the families taking part in the pod. Parents will receive session notes for their students, so they are constantly kept in the loop. For ACT, SAT, SSAT, ISEE, and HSPT test prep, students are required to have their own set of course books which VHES will provide.
____________________________________________________________________
Academic Coaching
DOES YOUR CHILD STRUGGLE WITH STAYING ORGANIZED, PLANNING SCHOOLWORK, OR STUDYING FOR EXAMS? CONTACT US FOR A FREE COACHING ASSESSMENT.
Vint Hill Educational Services offers academic coaching for students who have difficulty getting motivated, staying focused, or keeping up in school. With backgrounds in counseling, mentoring, teaching, and special education, our coaches are highly experienced at working with youth and helping students overcome a wide spectrum of challenges.
Academic coaching is especially beneficial for individuals with attentional problems, low executive functioning, or learning or cognitive disabilities—though it is also valuable for those struggling to deal with the ordinary stressors of understanding complex information, planning assignments, studying for exams, or transitioning to college. Students who work with an academic coach typically require guidance and assistance in:
· Getting and staying organized
· Planning coursework and managing time effectively
· Starting and completing schoolwork
· Studying and reading with proficiency
· Managing stress, anxiety, and distractibility
· Balancing academic and personal responsibilities
· Preparing for tests
Our coaches complete assessments to identify the student’s challenges, strengths, goals, and learning style. They then create customized plans that integrate a variety of tools and techniques to help build confidence and improve school performance. Strategies include positive reinforcement, setting achievable goals, optimizing skills, breaking down tasks, creating a supportive environment, and tracking progress.
We select the best coach for your child and provide a coach profile for you to review and approve. The coach matching process considers the coach’s education, experience, and personality, as well as the student’s issues, schedule, and preferred location (e.g., home, office, public library). Each session is one hour in length and one-to-one for individualized support. Parents receive access to our online Teachworks system, allowing them to review coaching session notes, receive session email reminders, and keep track of used and remaining session hours.
____________________________________________________________________
Test-Prep
Vint Hill Educational Services offers test preparation for the ACT, SAT, PSAT, SSAT, ISEE, HSPT, and SAT Subject Tests. Each session is one-to-one for individualized support. The tutor will assign one to two hours of test prep homework after each session. The sessions are ninety minutes in length and test prep materials are included. The tutor will focus on the student's weakest areas of the test. In order to ensure improvement, the student will continue to take full-length practice tests throughout the course. The student will also learn tips and test-taking strategies.
2020-2021 MOCK ACT/SAT TEST DATES
AS OF AUGUST 2020, WE WILL BE PROCTORING TESTS VIRTUALLY ON SATURDAY MORNINGS AT 9:00 AM. UPON REGISTERING FOR A VIRTUAL MOCK TEST, YOU’LL RECEIVE A TEST PACKET VIA USPS MAIL.
PACKET INCLUDES:
ACT/SAT ANSWER SHEET
ACT/SAT TEST BOOKLET
*ACT/SAT ESSAY PROMPT
FOUR PAGES OF LINED PAPER
TEST INSTRUCTIONS
*THE ACT/SAT ESSAY IS OPTIONAL. STUDENTS INTERESTED IN TAKING THE ACT/SAT ESSAY WILL CONTINUE ON WITH THE TEST AFTER THE FINAL MULTIPLE-CHOICE SECTION (ACT SCIENCE OR SAT MATH).
PLEASE SIGN UP NO LATER THAN MONDAY DURING THE WEEK OF THE MOCK TEST. BE SURE TO INCLUDE YOUR ADDRESS DURING REGISTRATION, SO THAT WE CAN MAIL YOU A TESTING PACKET.
ALL ACT/SAT TESTS WILL BE PROCTORED VIRTUALLY THROUGH LESSONSPACE. THE DAY BEFORE EACH TEST, STUDENTS WILL RECEIVE AN EMAILED LINK TO JOIN THE VIRTUALLY PROCTORED TEST. THE TEST INSTRUCTIONS CAN BE USED SHOULD A STUDENT LOSE CONNECTION TO THE TESTING LOBBY.
ACT
Register for a mock ACT by clicking on a specific test date below.
Mock ACT test dates:
SAT
Register for a mock SAT by clicking on a specific test date below. :
Mock SAT test dates:
We also offer one-to-one mock testing at our offices. This consists of a full-length practice test for your child. Tests include: ACT, SAT, PSAT, SSAT, ISEE, HSPT, and SAT Subject Tests. We provide the test booklet, essay booklet, answer sheet, testing timer, calculator, and pencils.
We can send parents a practice test as well, to administer to their student in-home. We will send out a free practice test packet along with proctoring instructions. Parents must send the answer sheet back to us via email or mail.
10 Tips for Parents Navigating the New Realities of Online Education
With COVID-19 causing widespread school closures, children across the country are being given alternate resources, some online, to study outside of the classroom. Temporary solutions being devised for remote education range from online classroom tools like Google Classroom, to Zoom and podcasts by teachers. While parents are adjusting to this new scenario, during this time it’s also important to help kids stay focused on learning and avoid overuse of games, social media, and videos. Read on for 10 tips.